INDEX FOR THIS PAGE
-
Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
-
Nature of the C-X Bond
-
Halogenation of Alkanes
-
Mechanism of Halogenation
-
Energetics of Halogenation
-
Regioselectivity of Bromination
-
Regioselectivity of Chlorination Compared to Bromination
-
Allylic Halogenation
-
Resonance Stabilization of the Allyl Radical
- Essentially, the naming of alkyl halides is not different from the naming of alkanes. The halogen atoms are treated as substituents on the main chain, just as an alkyl group, and have no special priority over alkyl groups.
- The name of a chlorine substituent is "chloro", that of a bromine substituent "bromo" and so on.
- You sould practice naming a variety of haloalkanes.
POLARITY AND STRENGTH OF THE
CARBON-X BONDS
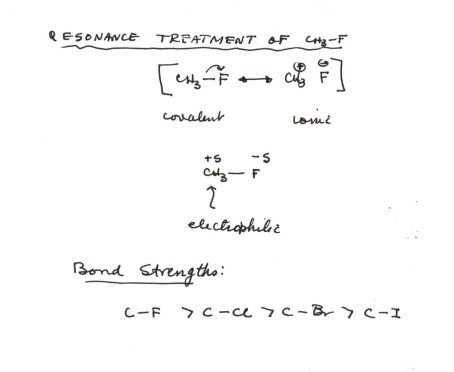
- Carbon-halogen bonds are very substantially polar covalent, with carbon as the positive and halogen as the negative end of the dipole. Conosequently, the carbon attached to the halogen is electrophilic. We shall see in the next chapter how nucleophiles react at the carbon of an alkyl halide.
- The carbon-fluorine bond is the strongest, especially since fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens, resulting in a larger contribution of the polar (ionic) structure to the resonance hybrid. The larger contribution of the ionic structure not only makes the molecule more polar, it also makes the bond more stable because the ionic structure is lowered in energy. However, all of the C-X bonds are significantly polar.
- The C-X bond dissociation energies (D), which you do not need to memorize, are C-F 108; C-Cl 85; C-Br 70; C-I 57 (these are for CH3-X bonds).
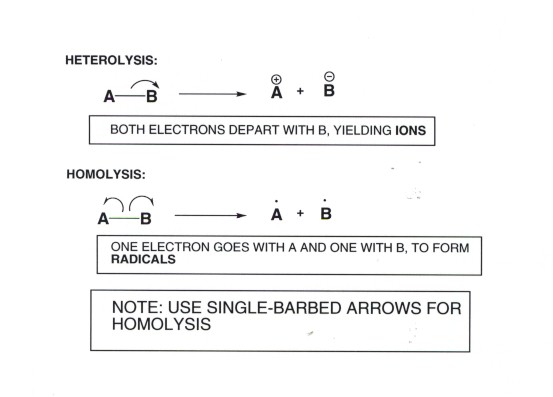
RADICALS: DEFINITION: SPECIES WHICH HAVE AN UNPAIRED ELECTRON (AN ODD NUMBER OF ELECTRONS)
FORMATION OF RADICALS BY HOMOLYSIS
THE METHYL RADICAL
The methyl radical is an example of a very simple organic radical. The carbon atom has only three hydrogens bonded to it, so it is trigonally hybridized. It therefore is planar and has the odd (unpaired) electron in the 2p AO. This odd electron is what makes the radical very reactive.
RELATIVE STABILITIES OF METHYL, PRIMARY, SECONDARY, AND TERTIARY RADICALS.

NOTE THAT THE D'S OF C-H BONDS DECREASE PROGRESSIVELY AS THE NUMBER OF ALKYL GROUPS ATTACHED TO THE RADICAL CENTER IN THE PRODUCT RADICAL IS INCREASED. THE D IS DECREASED BECAUSE THE PRODUCT RADICAL IS BEING STABILIZED BY THE ALKYL GROUPS.
HYPERCONJUGATIVE RESONANCE STABILIZATION OF A RADICAL CENTER BY ATTACHED ALKYL GROUPS

THE HALOGENATION REACTION
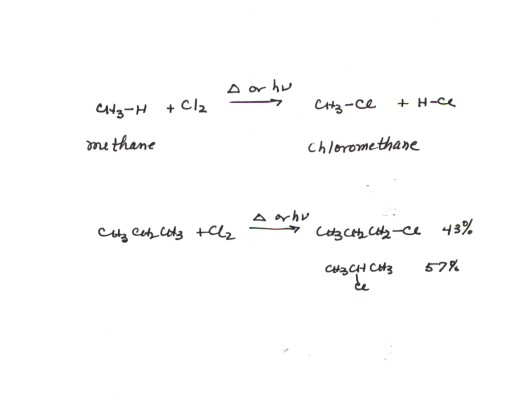
- A very simple example of the halogenation of alkanes is the chlorination of methane, as shown in the illustration below. The products are HCl and chloromethane.
- The REACTION TYPE is SUBSTITUTION, since a hydrogen of methane is replaced by a chlorine atom. The MECHANISTIC TYPE, as we will see, is Homolytic or Radical. The overall designation of the reaction, then, is SH (S WITH A SUBSCRIPT H).
- Virtually any C-H bond in which the carbon atom is tetrahedrally hybridized can be chlorinated, so that chloromethane can be further converted to dichloromethane, and this on to trichloromethane (chloroform), and finally to tetrachloromethane (carbon tetrachloride). You may recognize these chlorinated compounds as common solvents, both in the laboratory and in commercial uses.
- In the chlorination of alkanes more complex than methane or ethane, more than one monochloroalkane can be formed. We will refer to the preference for the formation of one constitutional isomer over the other as regiospecificity. For example, propane can be converted to both 1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane. Actually, both are formed, but the 2-chloropropane is slightly, but only slightly, preferred. Thus, the reaction is not very stereooregiospecific.
MECHANISM OF CHLORINATION OF METHANE
The mechanism for the chlorination of methane is representative of the chlorination of any alkane or indeed of the halogenation of an alkane:
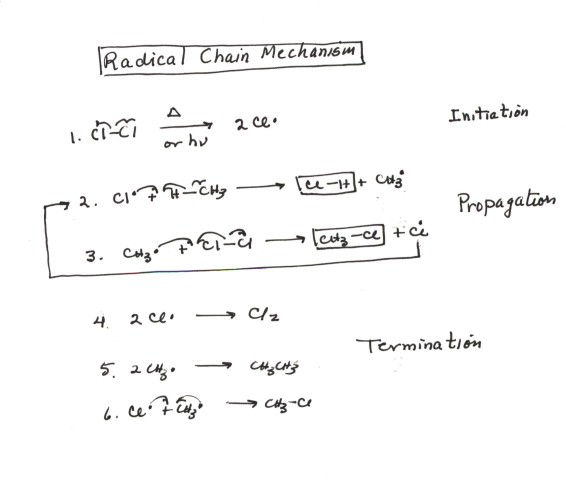
- This is our first example of a reaction mechanism in which radicals are involved. The definition of a radical is any species which has an unpaired or odd electron. There are two radical species involved in this mechanism, the chlorine atom and the methyl radical. The naming of organic radicals is simple, it is essentially the name of the corresponding substituent with the name radical being appended to it.
- The overall reaction is said to be a homolytic substitution reaction, as noted previously, because the bonds which are broken are broken homolytically, i.e., one electron departing with each component of the bond. In homolytic cleavages radicals are always formed, so the reaction mechanism can also be called radical substitution.
- One specific way in which radical reactions can occur is by means of a radical chain reaction. It is important to keep in mind that not all radical reaction mechanisms are radical chain mechanisms. A radical chain mechanism is one in which a particular set or two or three steps is repeated over and over without the necessity of generating more radicals. This is seen in steps 2 and 3 of the mechanism above. The stage of the reaction which represents the chain is called the propagation cycle. It is so called because in it, the observed products (HCl and chloromethane) are propagated or made. An efficient set of progpagation reactions is essential to a successful radical chain mechanism.
- Overall, this or any, radical chain mechanism consists of three discrete stages or parts. The first part is called initiation. In the initiation stage of the mechanism (step 1), the radicals which are necessary to enter the propagation cycle are generated. This typically involves the homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond, and so it requires energy. In this case, it is the Cl-Cl bond which is cleavaged homolytically.It is for this reason that the chlorination reaction requires the input of either heat or photochemical energy.
- As noted above, the second stage or part of the radical chain mechanism is the propagation cycle. An efficient propagation cycle uses a relatively few radicals to generate a large amount of product. It is desirable that for each radical produced in the initiation reaction, hundreds or even thousands of product molecules be generated before the radical is destroyed.
- The third and final stage of the radical chain mechanism is termination. Termination is the undesirable but unavoidable coupling between two radicals which destroys the chain carrying radicals and stops the current radical chain. It is thus the competitor of propagation. Because of this continuing consumption of radicals, initiation must continue to progressively generate more radicals. For a chain reaction to be effective, propagation by the radicals must be much more efficient than coupling between them.These coupling reactions are extrememly fast, because no bond is broken and one bond is formed. However, since the radical concentrations are extremely small, the probability of one radical meeting another is much less than for a radical to meet a molecule of chlorine or methane.
ENERGETICS OF THE REACTION AND THE INDIVIDUAL PROPAGATION STEPS

- First we note that the overall reaction is strongly exothermic and proceeds to the right. If it were endothermic it would not proceed toward products, no matter what the reaction mechanism. Of course, it is really the free energy change which determines the position of the equilibrium between reactants and products, but the enthalpy change is normally the largest component of this.
- Then, we note that both propagation steps are exothermic. This is , of course, a necessary but not sufficient condition for a rapid rate. However, radical reactions which are exothermic typically are very fast. It is important to note that both propagation steps are required to be very fast, since they must follow each other sequentially in the chain process.
- The hydrogen abstraction step (abstraction in this context means "pulling off") of the reaction is favorable because the HCl bond is stronger than virtually any C-H bond of an alkane.
- The second propagation step, in which methyl radicals abstract a chlorine atom from chlorine molecules, is even more favorable, because the relatively weak Cl-Cl bond is much weaker than the C-Cl bond formed. This weak Cl-Cl bond is also the main reason the overall reaction is favored.
- Of course, the termination steps are always powerfully exothermic, and the initiation is normally strongly endothermic.
REGIOSELECTIVITY IN BROMINATION
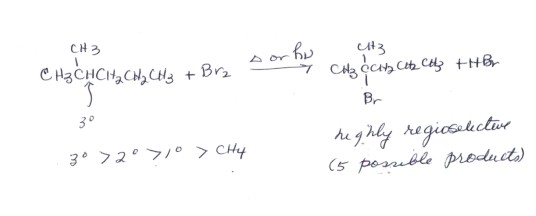
- There are primary,secondary, and teritary hydrogens in the alkane illustrated and five possible products of monobromination (not to mention many more di-, tri-, and polybromination bproducts). However, essentially only one product is formed, that being from substitution of the tertiary hydrogen by bromine. This highly regiospecific reaction is therefore synthetically quite useful. In contrast, chlorination gives all five products in significant amounts and is nearly useless for laboratory synthetic purposes.
- In general, tertiary hydrogens are most reactive to bromination. Secondary hydrogens are much less reactive, and primary ones are virtually unreactive, as are the hydrogens of methane.
- In sharp contrast, any of these types of hydrogen can be readily chlorinated, and the preferences are still tertiary>secondary>primary>methane, but the selcectivity is low. Note that vinyl C-H are very difficult even to chlorinate. (Why?)
WHAT IS THE BASIS FOR THE SELECTIVITY OF BROMINATION?
To understand the high selectivity of bromination and also the preference for tertiary over secondary, etc. hydrogens we should construct a TS model for the hydrogen abstraction step. This is the step of interest because once the hydrogen is removed, giving an alkyl radical, the bromine will be abstracted by the radical site. Thus, whichever hydrogen is abstracted will be replaced directly, at the same carbon, by bromine.

- The TS model is constructed in the usual way, using resonance theory and modeling the TS as a resonce hybrid of reactant-like and product-like structures. The DL/PC structure reveals partial bonds between H and Br and also between R and H, with partial radical character at both bromine (as in the reactant) and carbon (as in the product).The TS thus has alkyl radical character.
- It has already been established that tertiary alkyl radicals are more stable than secondary than primary than methyl, so as the R group (alkyl) is varied from tertiary to secondary to primary, the TS becomes less stable, the activation energy higher, and the rate lower.
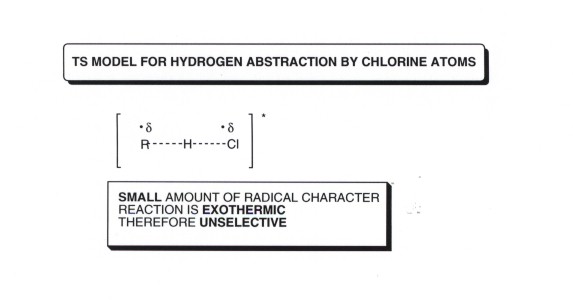
- This explains the sequence of reactivity, but not the degree of selectivity, which is high for bromine. To explain this, we need to use the Hammond Postulate as applied to this reaciton step. Since the H-Br bond strength is only about 87 kcal/mol and since any C-H bond of the tertiary, secondary, etc. types is stronger than this, the reaction is endothermic, and according to the Hammond Postulate, the TS more closely resembles the product. In the product-like structure, the radical character is on the alkyl group. Thus, we have extensive radical charcter development in the TS for the hydrogen abstraction step of bromination, which means the preference for tertiary hydrogens is relatively great.
REGIOSELECTIVITY IN CHLORINATION
- As we have earlier noted, chlorination has the same qualitative sense of selectivity as bromination, i.e., tertiary>secondary>primary, but the selectivity is very much lower.
- The TS model is essentially like that for bromination, having alkyl radical character, thus explaining the preference for tertiary hydrogens.
- The low selectivity is explained by the circumstance that the TS has only a low level of radical character. The basis for this conclusion is that the hydrogen abstraction step when chlorine atoms is involved is exothermic, since the H-Cl bond formed is relatively strong (D=103 kcal/mole), and stronger than any of the C-H bonds of alkanes except that of methane. Thus, an application of the Hammond Postulate to this TS reveals that it should have only a low level of radical character, i.e., it looks more reactant-like.
STATISTICAL EFFECTS IN CHLORINATION
- The chlorination of isobutane, in contrast to the bromination, which gives only tert-butyl bromide, gives rise to a mixture of isobutyl and tert-butyl chlorides, with the former (isobutyl chloride) actually predominating. How can it be explained that primary hydrogens are actually more reactive than tertiary ones?
- The answer lies in statistical or probability factors. In isobutane there is only one tertiary hydrogen but nine primary ones. The probability of a chlorine atom colliding with and abstracting a primary hydrogen is therefore nine times as great as with a tertiary hydrogen. Since the selectivity for a tertiary hydrogen over a primary one is relatively small in chlorination, it may be no surprise that the statistical factor of 9 which operates to prefer primary hydrogen abstraction is dominant over the small chemical selectivity which favors the tertiary hydrogen.
- If we compare the reactivity per hydrogen, we do see that there is an inherent preference for abstracting a tertiary hydrogen.
- In the case of bromination, the chemical selectivity is so high that it overwhelms the statistical factor of 9.
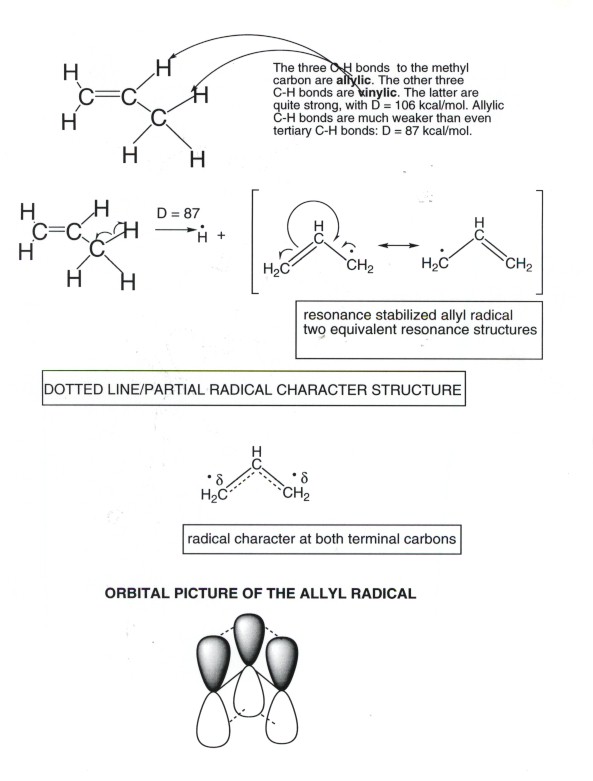
- Allylic hydrogens are hydrogens, such as the methyl hydrogens of propene, which are attached to a carbon atom which, in turn, is attached to a carbon-carbon double bond(see illustration below).
- Allylic hydrogens are especially easily halogenated by a free radical chain mechanism because their C-H bond dissociation energyies are relatively low, i.e., these bonds are weak and easy to break homolytically. We will see in a minute that this is because the allylic radicals produced upon homolysis are highly resonance stabilized.
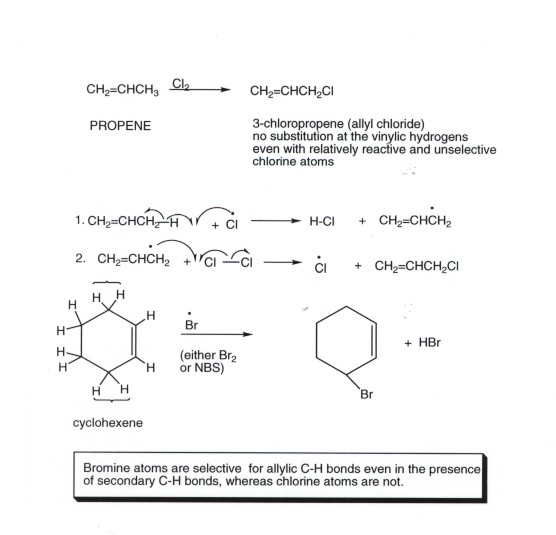
- If we consider propene itself, there are three equivalnet allylic hydrogens with D's of 86 kcal/mol, i.e., they are weaker than even tertiary C-H bonds. The other three bonds are of the vinyl type (i.e., they are directly attached to a carbon atom of the double bond) and have D's of ca. 106 kcal/mol, i.e., they are stronger than even the C-H bonds of methane and also of than that of HCl. Therefore, these particular bonds are not easy to halogenate, even by chlorination. Therefore, the only monohalogenation product of propene which is observed is 3-chloropropene or allyl chloride.
- The mechanism of chlorination or bromination is the same as before, the free radical chain mechanism. You should write this out for the specific case of propene.
- Any hydrogen atom which is of the general allylic type is especially easily halogenated, e.g., in the illustration below, the allylic halogens hydrogens of cyclohexene.
- The biggest problem with allylic halogenation is the electrophilic addition of the halogen to the C=C double bond. For bromination, this is usually overcome by using, instead of molecular bromine (dibromine), the compound N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), which is a less toxic and more conveniently handled solid, which produces bromine only very gradually in solution. Under these conditions (very low bromine concentration), allylic bromination by a free radical mechanism is normally predominant over electrophilic addition of halogen.
RESONANCE STABILIZATION OF THE ALLYL RADICAL
- Considering the illlustration given below, we note that the allyl radical has two equivalent resonance structures. Therefore, resonance stabilization is particularly strong.
- Note from the diagram that the MO's of the allylic pi system are delocalized over three carbons, so that it is impossible to designate the electrons as being shared by only two atoms, as in a classical covalent bond.
- The radical character appears equally upon the two terminal allylic carbons, but not at all on the central carbon. thus, the allyl radical reacts at the terminal carbon when it behaves as a radical, e.g., abstracting chlorine from chlorine molecules.
- The strong resonance stabilization of the allyl radical is the reason that the D for the allylic hydrogens of propene and other allylic hydrogens is much smaller than for typical hydrogens attached to carbon.
- Allylic radicals are more stable than tertiary radicals, than secondary, than primary , than methyl radicals.
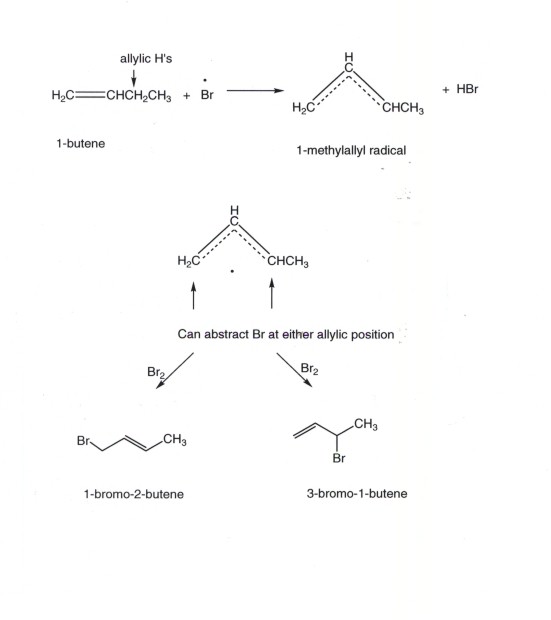
Regiochemistry of Allylic Halogenation
It is important to note that, because allylic radicals are delocalized over three carbon atoms and have radical character at two carbons (the terminal ones), when an unsymmetrical alkene is NBS brominated, two products can and do result.
RADICAL CHAIN ADDITION OF HYDROGEN BROMIDE TO ALKENES.
BACK TO THE TOP OF THIS PAGE